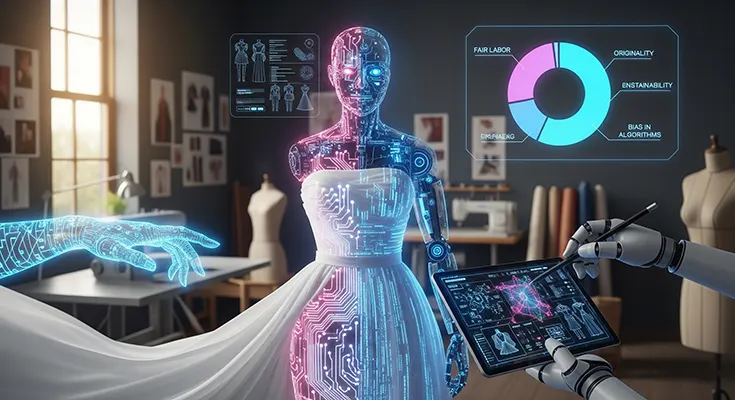
The fashion industry has always been a dynamic blend of art, culture, and innovation. Recently, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in creative fashion designs has opened new horizons in creativity, efficiency, and personalization. However, as AI takes a more prominent role in fashion design, several ethical considerations have emerged that industry professionals, designers, and consumers must address.
1. Intellectual Property and Originality
One primary ethical concern involves intellectual property rights. When AI systems generate fashion designs, questions arise about the ownership of these creations. Since AI algorithms often learn from existing works, there is the risk of unintentionally replicating designs or patterns protected by copyright laws, leading to accusations of plagiarism. Designers and companies must consider how to attribute authorship and protect original content while leveraging AI-generated designs.
2. Creativity vs. Automation
AI in fashion design poses philosophical questions about the nature of creativity. While AI can analyze vast amounts of data and produce innovative patterns or styles, it lacks human intuition and emotional expression. Over-reliance on AI risks reducing the artistic element in fashion, potentially making designs formulaic or lacking in cultural and emotional depth. Striking a balance between human creativity and AI automation is essential to maintain the industry’s artistic integrity.
3. Bias and Diversity
AI systems are only as unbiased as the data they are trained on. If the datasets used to train AI models predominantly feature certain cultures, body types, or aesthetics, the generated designs might perpetuate stereotypes or exclude diverse representations. Ethical AI usage in fashion requires careful curation of diverse training data to ensure inclusivity and to celebrate a wide range of cultural and individual identities.
4. Environmental Impact
While AI can optimize design processes and reduce waste by predicting consumer preferences, the computational power required for complex AI models also contributes to environmental concerns due to energy consumption. Ethical considerations include weighing the environmental costs of deploying AI against the sustainability benefits it might offer, such as producing on-demand designs that minimize overproduction.
5. Transparency and Consumer Trust
Consumers increasingly want to know how their products are made and designed. Transparency about the role of AI in creating fashion items helps build trust and allows customers to make informed choices. Ethical fashion brands must disclose AI involvement and clarify how it complements human creativity, ensuring that customers are not misled about the origins of their garments.
6. Job Displacement
AI’s introduction in fashion design poses potential risks to employment, as certain design tasks may become automated. This raises ethical questions about supporting designers and creative professionals through training and transition opportunities, rather than simply replacing human talent with machines.
The ethical considerations of using AI for creative fashion designs are complex and multifaceted. While AI offers exciting possibilities for innovation and efficiency, fashion brands and designers must navigate challenges related to intellectual property, creativity, inclusivity, environmental impact, transparency, and employment. By thoughtfully addressing these ethical issues, the fashion industry can harness AI’s benefits while preserving the human touch and cultural richness that define great design.